The ever-evolving finance and investment landscapes have been significantly impacted by decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DAOs are causing a paradigm shift in the traditional venture capital sector. Blockchain technology enables the growth of these disruptive organizations, which are redefining venture funding and management. DAOs showcase decentralized governance, transparent decision-making, and unique funding approaches. These aspects revolutionize access to capital for entrepreneurs and early-stage investor participation. In this article, we delve into DAOs in venture capital, focusing on their potential to transform the industry, their benefits, challenges, and real-world use cases in shaping funding innovation and entrepreneurship.
Evolution of Venture Capital
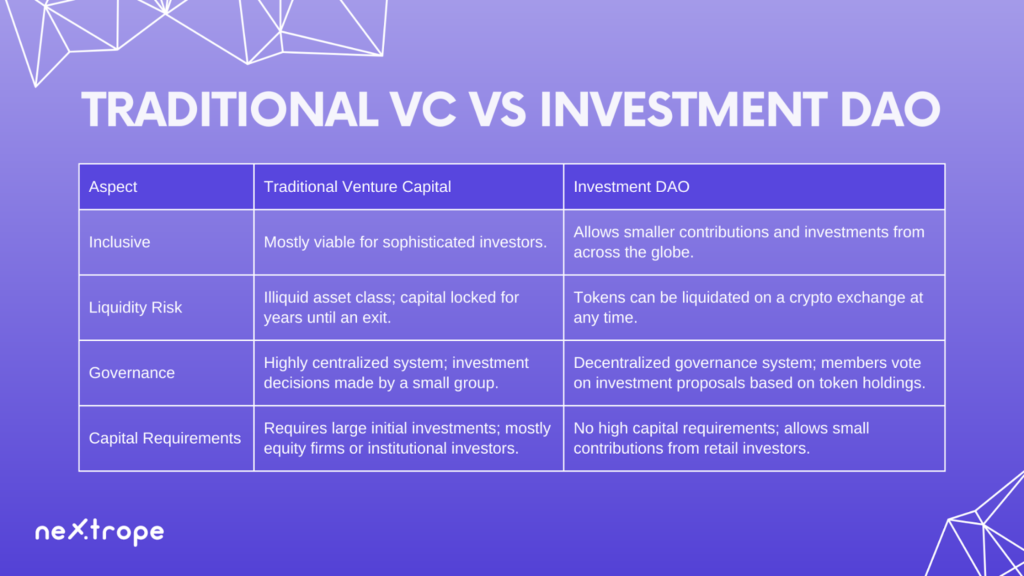
Understanding DAOs in venture capital impact requires grasping traditional investment models' evolution. Traditional venture capital features centralization, with few investors controlling funding decisions. This creates entry barriers for entrepreneurs and limits opportunities for a few favored people. Decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain technology birthed a more inclusive, accessible option. DAOs use smart contracts and consensus-driven governance, disrupting the venture capital scene. Decentralization principles position DAOs as a new venture capital frontier, enabling a democratic, transparent funding process for innovative projects.
DAOs in Venture Capital and Funding
DAOs represent a paradigm shift in how companies raise capital and manage their operations. They open up new possibilities for venture capital and funding by bringing the following features to the table:
- Decentralization: DAOs distribute the decision-making authority among its members, eliminating the need for intermediaries or centralized authorities. This makes the funding process more efficient and transparent.
- Tokenization: DAOs use cryptographic tokens to represent ownership or voting rights. This enables investors to have a direct say in the operation and governance of their investments. (Interested in DAO tokenomics? Check out our article!
- Smart Contracts: DAOs utilize smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automate many processes, reducing the need for manual intervention and potential for human error.
- Global Access: Given their decentralized nature, DAOs enable anyone, anywhere, to participate in venture capital funding. This widens the pool of potential investors and fosters global collaboration.
Investment DAO
DAO is transforming the VC industry. Investment DAOs are crucial for sourcing, evaluating, and managing investments. They use blockchain and smart contracts for a democratic, transparent process. DAOs in venture capital pool funds from contributors. This allows for collective decision-making and capital allocation to projects.
A wider range of investors can join early-stage investments. Investment DAOs offer platforms for knowledge sharing and due diligence. This leads to more informed decision-making. Decentralized governance replaces traditional middlemen in these organizations. Investment DAOs have the potential to change the VC industry significantly, promoting innovation and growth for startups inclusively and cooperatively.
More about this topic
Traditional Venture Capital vs Investment DAO
Success Stories
DAOs in venture capital have made a mark through various success stories, showcasing DAOs' transformative potential in venture capital for innovative projects funding.
MetaCartel Ventures, a pioneering investment DAO, invested in multiple blockchain startups. Their group approach evaluates opportunities, offers guidance, and utilizes networks to fast-track portfolio companies' growth.
Syndicate DAO is known for decentralized finance investments. With group decision-making and thorough research, they've backed Aave, Uniswap, and Compound projects, advancing the DeFi ecosystem.
OrangeDAO is a venture fund of past, present, and future Y Combinator founders who specialize in crypto. Orange DAO also helps startups apply to, and be accepted into Y Combinator, while helping mentor their leadership and recruit talent, and acquire customers.
The LAO, one of the first legal decentralized venture funds, has invested in numerous projects like NFT platforms, decentralized social networks, and blockchain infrastructure projects.
DAO.vc is a decentralized autonomous entity that acts as a service for a pool governed by shared voting on investment projects chosen using a predefined algorithm.
SeedClub is a DAO that builds and invests in communities. The mission of Seed Club is to assist web3 community builders. They are creating a future in which the value created by online communities is captured by people rather than platforms.
These achievements underline how investment DAOs disrupted traditional models by offering a more inclusive and decentralized platform. Investment DAOs have proven their capability to detect and support groundbreaking startups, redefining the future of venture capital.
Potential for Future Growth and Expansion of DAO-driven Venture Capital
The future of DAOs in venture capital and funding looks promising. As blockchain technology continues to mature, DAOs are likely to become more robust, secure, and user-friendly, attracting more participation from both investors and entrepreneurs. Furthermore, regulatory clarity around DAOs could also propel their growth in venture capital.
In the future, we may see more venture capital firms incorporating DAO structures to give their investors more direct control over their investments. We may also see more startups choosing to raise funds through DAOs instead of traditional venture capital, due to the transparency, global access, and democratized decision-making that DAOs offer.
Another potential area of growth is the integration of DAOs with DeFi (Decentralized Finance) platforms. This could open up even more avenues for decentralized funding and provide investors with new ways to earn returns on their investments.
Conclusion
In summary, DAOs are transforming the venture capital sector. They employ blockchain technology and decentralized governance for a new approach. This shift from traditional centralized models results in transparent decisions, inclusive capital access, and creative funding strategies.
Significantly, investment DAOs like MetaCartel Ventures, Syndicate DAO, and The LAO demonstrate the potential of DAOs in venture capital. They have successfully backed various projects, spotlighting their skill in discovering and fostering groundbreaking startups. Their accomplishments highlight the inclusive, transparent, and democratized decision-making offered by DAO-driven venture capital.
As we look forward, the prospects of DAOs in venture capital are bright. With blockchain advancements and changing regulations, DAOs will become more secure and accessible to a broader audience. Increased adoption of DAO structures by venture capital firms and startups is expected, as well as integration with decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. The transformative power of DAOs is creating a decentralized, inclusive, and transparent system that benefits both entrepreneurs and investors.
 en
en  pl
pl