The Arbitrum DAO stands at the convergence of technology and democratic decision-making, capturing the attention of the blockchain world. As we delve into this exploration, we'll examine the intricacies of DAOs and what distinguishes the Arbitrum DAO in this dynamic environment.
Understanding DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) are organizations governed by computer code embedded rules and stored on a blockchain. Unlike conventional organizations, DAOs operate without centralized authority, making them resistant to single points of failure or control.
Structure. Smart contracts, which are pre-established rules encoded on a blockchain, drive DAOs' operations. These contracts automatically execute when specific conditions are fulfilled, without any intermediary involvement.
Purpose. DAOs aim to facilitate a truly decentralized decision-making process in which every stakeholder has input. This democratic method ensures decisions are made to benefit the entire community rather than just a select few.
Function. Governance tokens are generally associated with DAOs. Token owners can propose amendments, vote on proposals, or assign their voting rights to someone else. The voting weight may be proportional to token holdings, enabling stakeholders of all sizes to have a say.
Arbitrum DAO
Arbitrum DAO represents more than just another instance of blockchain governance; it signifies an evolutionary leap in decentralized governance mechanisms, particularly concerning Ethereum scaling solutions.
Unique Features. Progressive decentralization is the distinguishing characteristic of Arbitrum DAO's approach. While enhancing Ethereum's transaction processes with Arbitrum Rollup and Arbitrum AnyTrust protocols, the DAO ensures that control over these protocols resides within its community.
The $ARB Token. The $ARB governance token is more than just a tradable commodity; it represents both a voice and a vote. Through this mechanism, stakeholders can influence Arbitrum's future by deciding on matters ranging from protocol updates to potential integrations.
A Vision Centered on Community. The driving force behind the DAO is community participation. The potential to shape the course of Arbitrum protocols lies with every token holder, developer, and enthusiast. By decentralizing decision-making power, the Arbitrum DAO showcases a model directed by many, not just a few.
It's crucial to appreciate that DAOs, particularly those like the Arbitrum DAO, represent more than just technological wonders. They embody a transformative shift in governance, decision-making, and community engagement. The DAO serves as both a reflection of our current position in the blockchain landscape and an indicator of our future direction.
Arbitrum DAO - Governance Mechanism
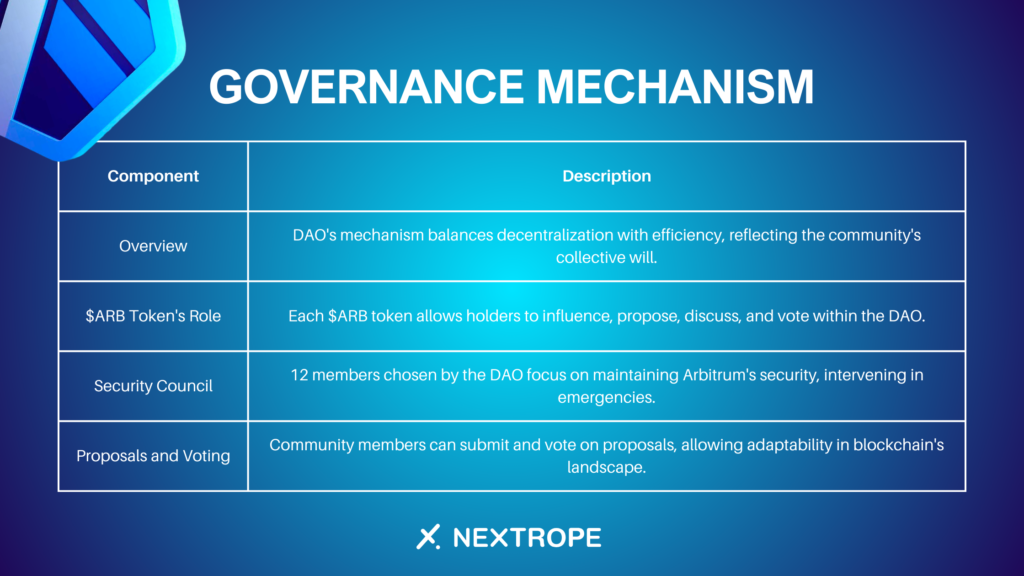
The cornerstone of the DAO is its powerful and inclusive governance mechanism designed to ensure that decisions reflect the collective will of its community members rather than being dictated by a select few. This multi-dimensional process carefully balances decentralization with operational efficiency.
The $ARB Token's Role. The $ARB governance token is more than just a digital asset; it is essential for decision-making within the DAO. Each token represents influence within the ecosystem, enabling holders to propose, discuss, and vote on various facets of the Arbitrum protocols.
Security Council and DAO Dynamics. Working alongside the broader DAO, the Security Council functions as a specialized group dedicated to safeguarding Arbitrum's security and performance. Chosen by the DAO, these 12 council members step in only during emergencies to maintain system resilience and stability.
Proposals and Voting. Community members have the freedom to submit proposals for consideration and voting. This democratic practice helps the DAO remain adaptable to the ever-changing needs of the blockchain realm.
Decentralization - Arbitrum DAO
In Arbitrum DAO, decentralization serves not merely as a trendy term but as its foundational principle and core strength.

Decision-making without alterations. Unlike centralized organizations where decision-makers can change or overturn decisions, Arbitrum DAO decisions remain permanent. Once the community reaches consensus, the blockchain solidifies it as an immutable and transparent record.
Diversity brings harmony. Decentralized systems let numerous voices, viewpoints, and skills influence each decision. This diverse input fosters innovative and thorough solutions that centralized approaches might miss.
The community drives evolution. As the blockchain landscape progresses, Arbitrum DAO does too. Community feedback directs this evolution, ensuring it stays relevant and adaptable through the strength of decentralization.
Engagement
Participation in the DAO goes far beyond token ownership; inherently, it means actively influencing its trajectory. Numerous opportunities exist for anyone who shares the organization's vision of a better future.

Delegate roles. Eager to shape the future of the DAO? Delegates have the chance to represent fellow token holders through active participation in decision-making processes and ensuring the collective voices of constituents are heard.
Joining discussions. Discord server facilitate lively debate, conversation, and idea generation. Ideas of every magnitude can find an attentive audience on these platforms.
Staying current and casting votes. Token holders who prefer a less active role still wield significant influence by keeping informed on current proposals and voting accordingly. Every vote has value, accurately reflecting collective desires in shaping the DAO's trajectory.
The living entity that is Arbitrum DAO continuously advances with each interaction, vote, and conversation. Embracing active participation and inviting each member to take a hand in shaping its future, it thrives on collaboration.
Conclusion
At its core, the Arbitrum DAO merges cutting-edge technology with democratic practices in perfect harmony. Rooted in decentralization, the organization symbolizes not only the revolutionary capabilities of blockchain but also provides a model for digital-age collective decision-making. The transparent, immutable, community-driven decision process exemplified by Arbitrum DAO bears an undeniable role in defining the way forward for decentralized ecosystems and beyond.
 en
en  pl
pl 












