Enter Chainlink, a decentralized oracle network that plays a pivotal role in bridging the gap between blockchain smart contracts and real-world data. Its relevance to gaming and NFTs is profound, particularly through its Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF). Chainlink's VRF brings a new level of integrity and fairness to the process of generating in-game items and NFTs, ensuring that the rarity and uniqueness of these assets are genuinely random and tamper-proof.
MUST READ: "What is Chainlink"
Understanding NFTs in Gaming

Explanation of NFTs and Their Unique Properties
NFTs, or Non-Fungible Tokens, represent uniquely identifiable assets that are verified on a blockchain. NFTs are distinct, with each token having a unique set of attributes and value. This uniqueness and the ability to prove ownership securely make NFTs particularly appealing for the gaming industry, where they can represent anything from in-game items and collectibles to characters and virtual land.
The Significance of NFTs in Gaming for Creating Rare and Unique In-Game Items
In gaming, NFTs bring fresh opportunities for both players and developers. Players gain genuine ownership of in-game assets, enabling trade, sale, or use across various games and platforms. Developers find new paths in game design, engagement, and monetization. Crafting rare and unique NFT items boosts the gaming experience, fosters community, and allows players to gain real-world value from gameplay.
Chainlink's Role in Enhancing NFT Rarity and Value
Overview of Chainlink Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF) and Its Importance
Chainlink VRF revolutionizes blockchain with secure, verifiable randomness, crucial for gaming and NFT minting. Its generated randomness is blockchain-verifiable, allowing independent audits to confirm its fairness and lack of external influence.
How Chainlink VRF Ensures the Fair Minting of Rare NFTs
For the gaming industry, Chainlink VRF ensures fair and transparent NFT minting. It helps determine the attributes and rarity of new NFTs, like character skins or weapons, guaranteeing equal chances for players to get rare items. This builds trust in the gaming community and boosts NFT value, as players trust the fairness of item acquisition.
Chainlink VRF: Revolutionizing Gaming Randomness
Chainlink's Verifiable Random Function (VRF) has emerged as a cornerstone technology for blockchain-based applications, particularly in the gaming sector, where randomness plays a critical role in various aspects ranging from character creation to in-game dynamics and rewards distribution.
Detailed Explanation of What Chainlink VRF Is and How It Works
Chainlink VRF combines block data that is still unknown when the request is made with the oracle node’s pre-committed private key to generate both a random number and a cryptographic proof. The VRF's smart contract will only accept the random number input if it has valid cryptographic proof, and the cryptographic proof can only be generated if the VRF process is tamper-proof. This ensures the randomness is provable and not manipulated, bringing fairness and transparency to the forefront of digital randomness applications.
Examples of Gaming Applications Utilizing Chainlink VRF for Randomness
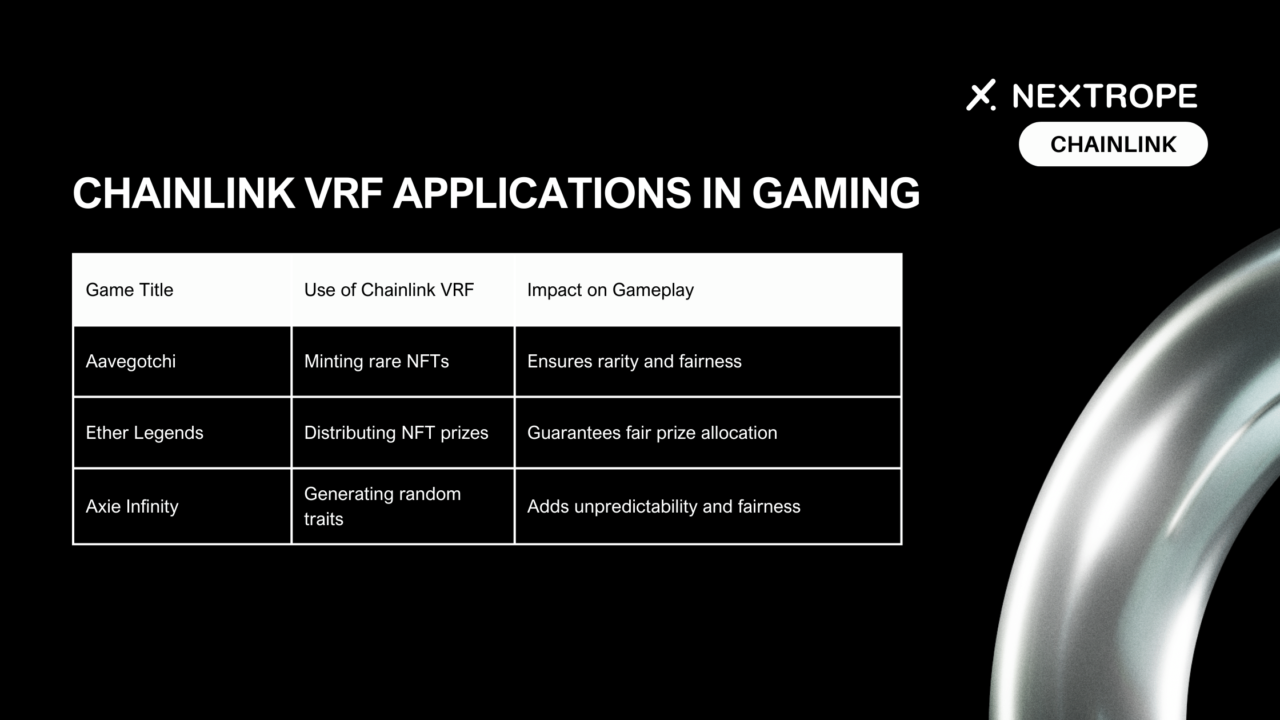
Case Studies:
- Aavegotchi. This blockchain game integrates Chainlink VRF to mint rare NFTs called "Aavegotchis," each with randomly selected attributes when a player opens a Portal. This process ensures the rarity and uniqueness of each Aavegotchi, making the game more engaging and the assets more valuable.
- Ether Legends. This digital collectible card game leverages Chainlink VRF to distribute rare crypto-backed NFT prizes to players. The randomness ensures fairness in awarding these prizes, making competitions more exciting and rewarding.
- Axie Infinity. Known for its vibrant digital pet universe, Axie Infinity uses Chainlink VRF to generate random traits for Origin Axies. This randomness adds a layer of unpredictability and fairness to the breeding and battling mechanics within the game.
The Advent of Dynamic NFTs
Dynamic NFTs represent a groundbreaking shift in the NFT landscape, offering assets that can evolve over time based on real-world events, player achievements, or other criteria.
MUST READ: "What is Dynamic NFT"
Introduction to Dynamic NFTs and Their Evolving Nature
Unlike traditional NFTs, which are static and unchanging, dynamic NFTs can alter in rarity, appearance, or utility. This is made possible by smart contracts that can update the NFT's attributes in response to external data inputs or on-chain events, facilitated by oracles like Chainlink.
Examples of Dynamic NFTs in Sports:
- MLB star Trey Mancini and NBA Rookie LaMelo Ball have both launched dynamic NFTs that change based on real-life performances and achievements. These NFTs not only serve as digital collectibles but also as living records of the athletes' careers, engaging fans in a novel and interactive manner.
GameFi and Chainlink

The fusion of decentralized finance (DeFi) and gaming, known as GameFi, creates a new realm where players can earn real economic rewards through gameplay.
Exploring the Intersection of Gaming and DeFi (GameFi)
Chainlink supports the growing gaming ecosystem in several ways. It provides reliable data feeds for managing in-game economies. It also offers secure random number generation to ensure fair gameplay. Additionally, Chainlink automates smart contract executions, streamlining decentralized gaming operations.
No-Loss Savings Games
A notable DeFi innovation in gaming is no-loss savings games. These games blend entertainment with financial growth opportunities.
PoolTogether as an Example
PoolTogether is a platform that illustrates this concept. It uses Chainlink VRF to randomly select winners in its no-loss savings game. In this game, users pool their funds to collectively earn interest. One lucky participant wins the accumulated interest. Meanwhile, all other players receive their initial deposits back. Chainlink's secure randomness drives this model, promoting transparency and fairness. This encourages broader participation.
Chainlink in Sports and Esports Betting
Blockchain technology enhances sports and esports betting with transparency and fairness, thanks to decentralized oracles like Chainlink. These oracles securely bring real-world data to the blockchain, essential for settling bets on actual game outcomes.
Key Takeaways

- Chainlink's Impact on Gaming and NFTs: Chainlink's technology, especially its Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF) and oracle services, has significantly impacted the gaming and NFT sectors by ensuring fairness, transparency, and trust in digital randomness and real-world data integration.
- Future Potential of Chainlink in the Gaming Industry: The potential for Chainlink to revolutionize the gaming industry extends into areas like dynamic NFTs, GameFi, and decentralized finance applications within gaming ecosystems.
Conclusion
The transformative potential of Chainlink's technology in gaming and related sectors like NFTs and betting is profound. By enabling fair and transparent randomness, verifiable real-world data integration, and dynamic asset capabilities, Chainlink is not just enhancing existing gaming and betting ecosystems but also paving the way for entirely new gaming paradigms. As the landscape of blockchain gaming and NFTs continues to evolve, Chainlink's contributions are foundational to its growth and sustainability.
FAQ
How does Chainlink's Verifiable Randomness Function (VRF) enhance the gaming and NFT sectors?
- Chainlink's VRF ensures fairness and transparency in generating in-game items and NFTs by providing genuinely random and tamper-proof rarity and uniqueness.
What are dynamic NFTs and how do they differ from traditional NFTs?
- Dynamic NFTs can evolve over time based on real-world events or player achievements, offering a more interactive and engaging experience compared to static traditional NFTs.
What integration challenges exist with Chainlink?
- Issues like scalability and adoption with traditional platforms.
How does Chainlink protect NFT transactions?
- Through secure data handling and fraud prevention mechanisms.
 en
en  pl
pl 












