Investors look for projects that not only develop innovative products but also do it sustainably. In a way that allows for long-term growth, and resistance to uneasy conditions in the crypto market. Projects can achieve this through a studious design of their tokenomics model.
Understanding Tokenomics
Tokenomics, short for token economics, refers to the study and design of economic systems within blockchain networks and crypto projects. At its core, tokenomics encompasses the distribution, circulation, and utilization of tokens to incentivize various stakeholders and drive desired behaviors within the ecosystem.
Key Components of Sustainable Tokenomics
Token Allocation
Defining clear purposes and rules for the treasury fund to align the interests is essential. A well-defined allocation strategy ensures that tokens are distributed in a good manner. That it promotes decentralization, fosters community participation, and supports the long-term growth of the ecosystem.
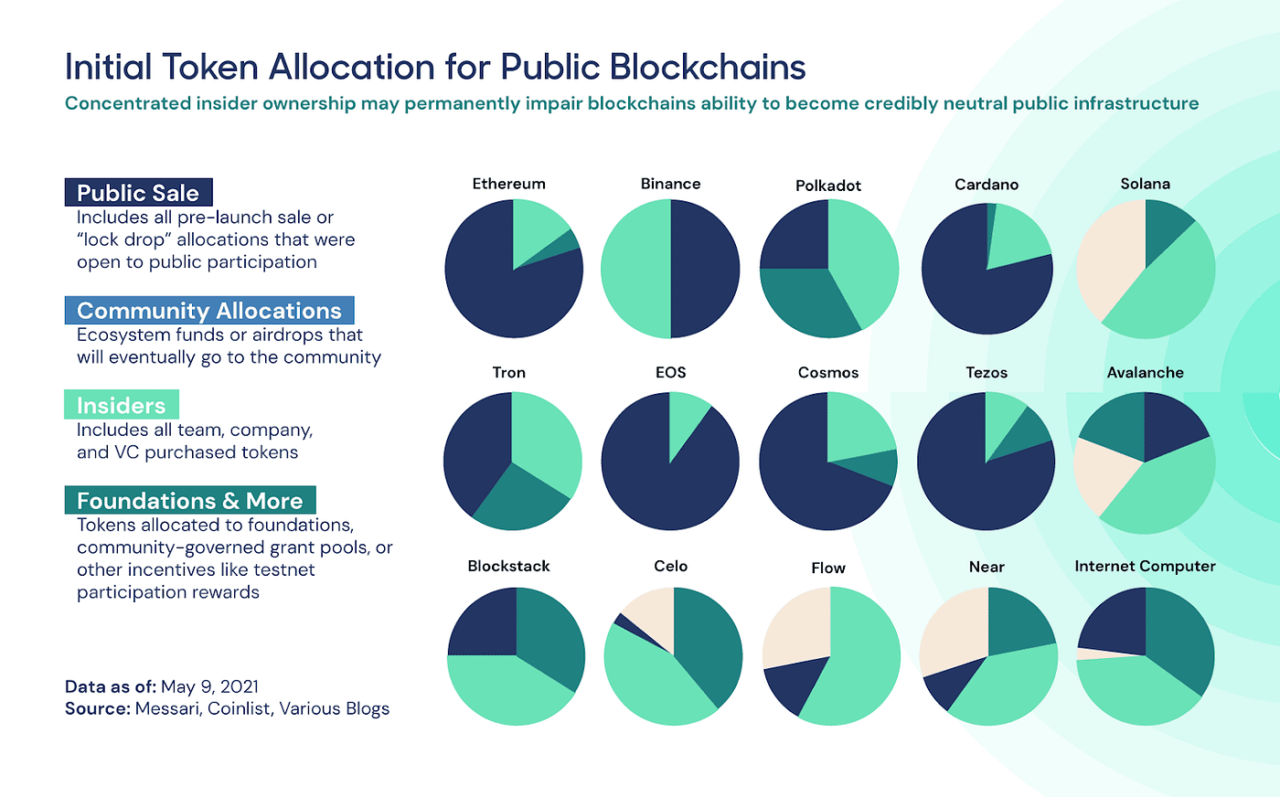
Maintaining a balanced token allocation to achieve decentralized governance and organic project growth is critical. By distributing tokens equitably among stakeholders, projects can mitigate the risk of centralization, and foster a diverse and engaged community. While it may be tempting to allocate most tokens for the founding team and institutional investors, projects should remember that the value of their tokens is in large part determined by how decentralized the ownership structure is.
Token Vesting Schedule
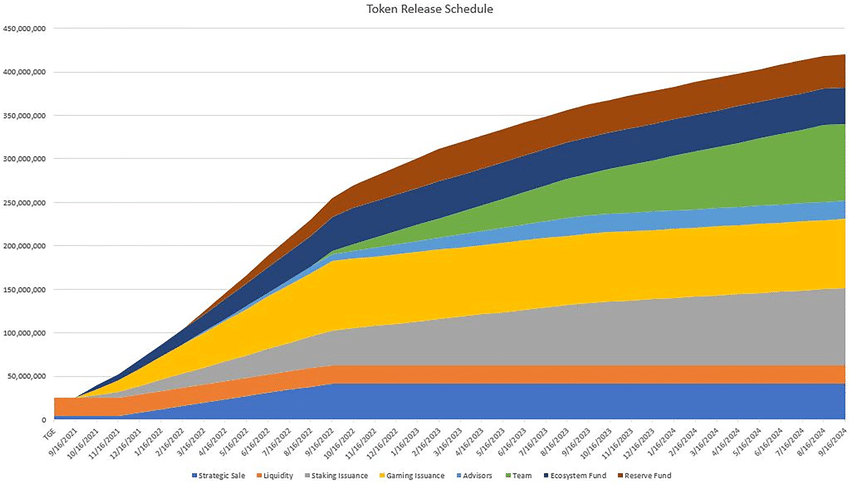
Implementing a structured vesting schedule for team members, investors, and advisors is crucial to ensure the alignment of incentives and commitment. A vesting schedule gradually releases tokens over a specified period, incentivizing continued participation and discouraging short-term speculation.
Maximum Inflation
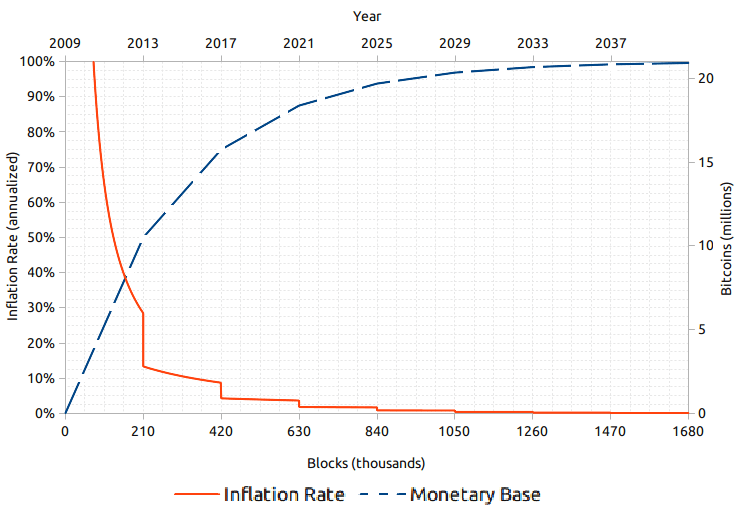
Managing inflation is a delicate balancing act for crypto projects, as excessive inflation can erode the purchasing power of tokens. Insufficient inflation may hinder growth and adoption. An important metric in that regard is Maximum Inflation, which refers to the total supply increase over time. It is calculated through dividing maximum supply by the initial supply.
Projects must carefully calibrate their inflationary policies to maintain a healthy balance between supply and demand. While also incentivizing long-term holding and participation. By adjusting maximum inflation rates in response to project needs, crypto projects can optimize tokenomics for sustainable growth and stability.
Value Accrual
Ensuring that tokens accrue tangible value to holders is essential for fostering long-term engagement and participation within the ecosystem. Value accrual mechanisms may include utility features, governance rights, revenue-sharing mechanisms, or other incentives that incentivize holding and active participation in the project.
Strategies for Designing Sustainable Tokenomics Models

Defining Clear Objectives
Establishing clear objectives and goals for the project's economic model is fundamental to its success. By articulating a compelling vision and roadmap, projects can attract stakeholders, align incentives, and rally support for their long-term mission. Clear objectives also provide a framework for decision-making and resource allocation, guiding the project towards sustainable growth.
Incorporating Governance Mechanisms
Implementing robust governance mechanisms is essential for ensuring democratic decision-making and community involvement in protocol upgrades and changes. By empowering token holders to vote on proposals, participate in governance discussions, and shape the future direction of the project, projects can foster a sense of ownership and accountability within the community.
Ensuring Transparency and Accountability
Promoting transparency and accountability in tokenomics design and fund management is critical for building trust and confidence among stakeholders. By providing regular updates, financial reports, and disclosures, projects can demonstrate their commitment to integrity
Case Studies: Examining Sustainable Tokenomics Models
Ethereum (ETH)
Ethereum, often regarded as the pioneer of smart contract platforms, boasts a robust tokenomics model that underpins its vibrant ecosystem. ETH serves as the native currency of the Ethereum network, facilitating transactions, powering decentralized applications (dApps), and serving as collateral for various DeFi protocols. With a clear distribution schedule, Ethereum incentivizes miners, validators, developers, and users to contribute to the network's security, scalability, and innovation.
Cardano (ADA)
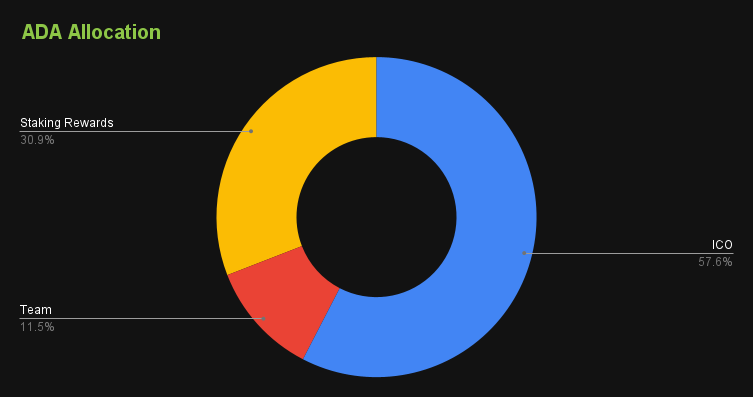
Cardano, one of the most prominent Layer 1 platforms, attributes much of its success to a tokenomics model focused on long-term growth. The platform itself states in its whitepaper: “The overall focus beyond a particular set of innovations is to provide a more balanced and sustainable ecosystem that better accounts for the needs of its users as well as other systems seeking integration”. Cardano tokenomics model supports sustainable development goals through research-based approach, decentralized governance structure, and well-thought treasury system. Unfortunately, commitment to sustainable growth came with a cost. Cardano Blockchain is much slower than many of its competitors, which reflects the famous blockchain trilemma (hypothesis that blockchain can’t be secure, scalable, and decentralized at the same time).
Challenges and Future Directions
Tokenomics has emerged as a powerful tool for incentivizing and coordinating decentralized networks. It also presents various challenges and areas for improvement. Addressing issues such as governance effectiveness, economic sustainability, and regulatory compliance will be crucial for advancing crypto projects, in the face of progressing regulatory scrutiny.
MUST READ: "Tokenization Regulations"
Conclusion
Tokenomics represents a foundational aspect of crypto and Web3 projects, providing the economic infrastructure needed to incentivize participation, coordinate activity, and drive value creation within decentralized networks. By designing sustainable economic models that align incentives, foster community engagement, and promote long-term growth, projects can get the best out of blockchain technology
If you're looking to design a sustainable tokenomics model for your DeFi project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com. Our team is ready to help you create a tokenomics structure that aligns with your project's long-term growth and market resilience.
FAQ
Why is token allocation important?
- Proper token allocation promotes decentralization and community engagement, vital for a project's success.
What's a token vesting schedule?
- A schedule ensuring stakeholders remain committed by gradually releasing their tokens over time.
How can DeFi tokens retain value?
- By implementing supply control mechanisms and expanding utility within the ecosystem.
What are key challenges in tokenomics design?
- Balancing incentives, managing inflation, and navigating regulatory landscapes are significant challenges.
 en
en  pl
pl 












