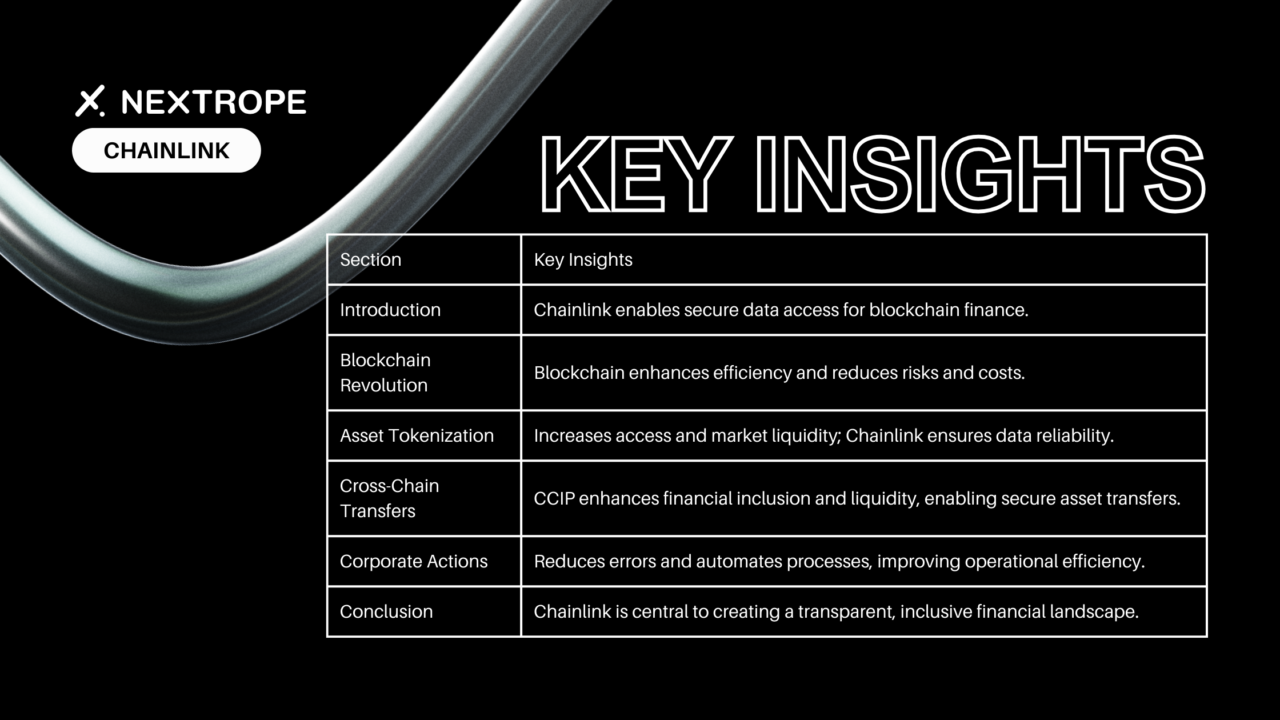
Chainlink within on-chain finance? The financial sector stands on the brink of a revolutionary transformation, driven by the rapid evolution of blockchain technology and the emergence of decentralized finance (DeFi). At the heart of this transformation is Chainlink, a decentralized oracle network that is pivotal in bridging the gap between traditional financial systems and the world of blockchain. Chainlink's technology enables secure, reliable, and timely access to real-world data for smart contracts, underpinning a variety of on-chain finance applications.
On-chain Finance: A Revolution in the Financial System

The advent of blockchain technology has ushered in a new era for the financial system, promising to replace outdated backend processes with modern, digitized solutions. This revolution is characterized by the automation of backend processes and the synchronization of multiple ledgers of record, which collectively have the potential to substantially reduce risk and enhance capital efficiency across the financial services sector.
MUST READ: "What is Chainlink"
The Potential of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers an unparalleled opportunity to reimagine and streamline the financial system's foundational operations. Its impact is profound, with the potential to:
- Reduce Operational Risks: By automating and digitizing backend processes, blockchain technology minimizes the risk of errors and fraud, ensuring a higher level of security and trust in financial transactions.
- Enhance Capital Efficiency: The synchronization of ledgers across the financial ecosystem allows for more efficient allocation and management of capital, reducing the need for intermediaries and lowering transaction costs.
- Cut Infrastructure Costs: The automation of backend office operations, as highlighted by Santander's report, could lead to substantial savings for banks, estimated at $15-20 billion annually. This reduction in costs stems from decreased reliance on manual processes and legacy systems, paving the way for a leaner, more agile operational model.
Asset Tokenization: Unlocking New Opportunities
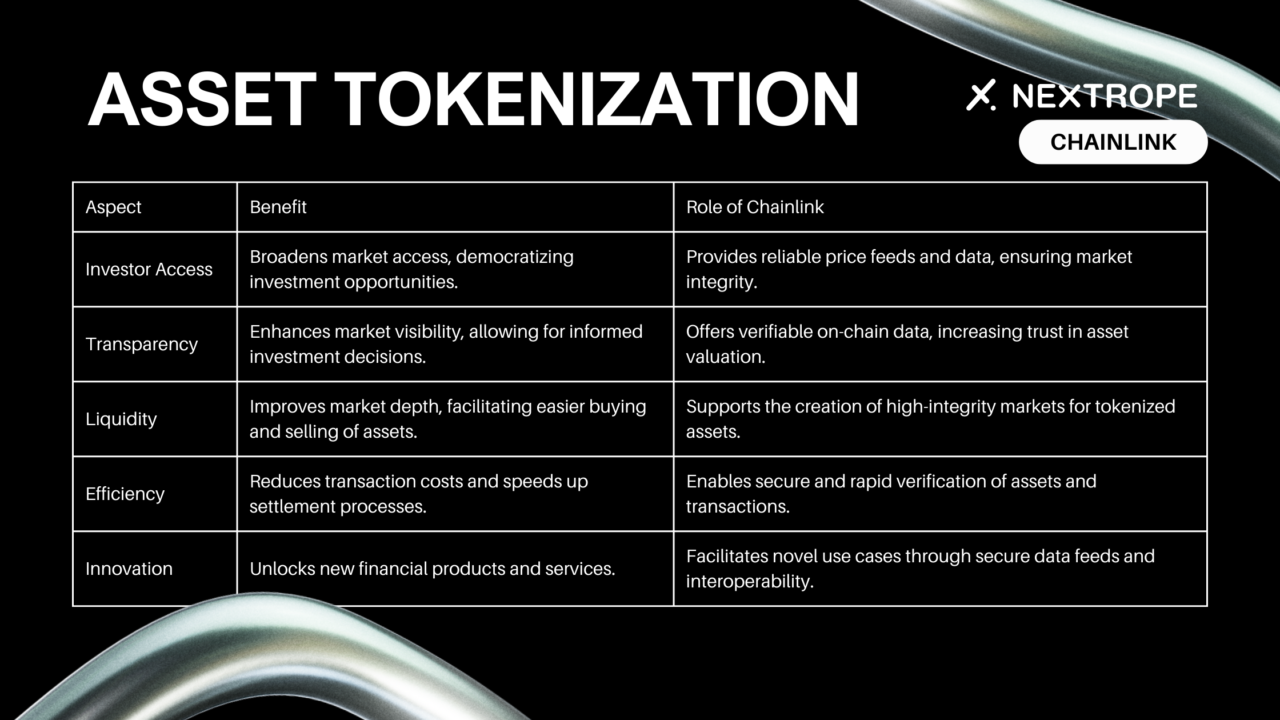
Tokenizing real-world assets broadens market access and liquidity, with Chainlink ensuring data reliability.
- Investor Access Increase: Tokenization opens markets to wider audiences, democratizing investment opportunities.
- Transparency and Liquidity Boost: Blockchain's transparency and token fungibility lead to more vibrant markets.
Chainlink champions this transformation, ensuring the reliable data and infrastructure necessary for robust on-chain markets. Its collaborations and technology underpin the sector's shift towards more accessible, transparent, and efficient financial systems. As blockchain and Chainlink technologies advance, their potential to reshape global finance becomes increasingly evident, promising a future of inclusivity and innovation.
Want to find out more about Chainlink Use Cases? Read "Chainlink in DeFi"
Cross-Chain Transfers: Enhancing Financial Inclusion and Liquidity
In the digital finance realm, Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) stands out. It forges connections between disparate blockchain networks. This advancement is pivotal for realizing blockchain's vision of boosting global financial inclusion and liquidity.
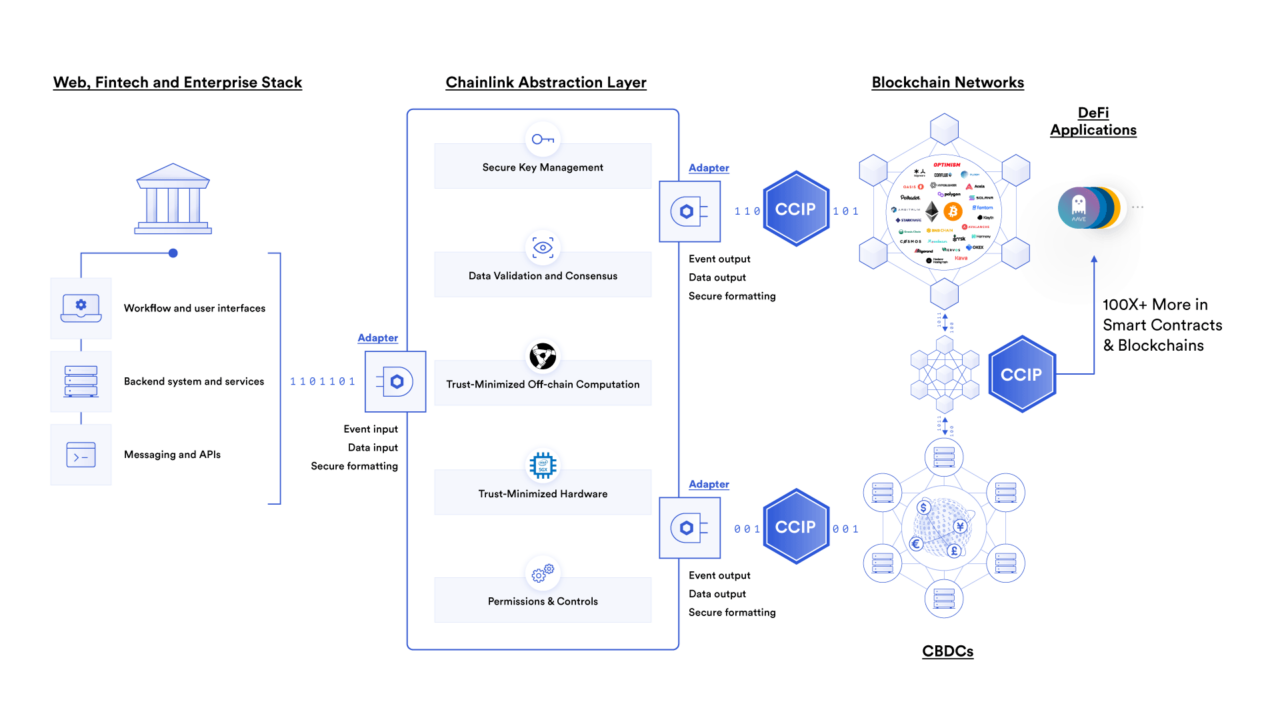
Secure and Efficient Asset Transfer
Through CCIP, financial markets worldwide become accessible. This inclusivity primarily aids those in developing regions, offering them financial opportunities once deemed unattainable. Moreover, CCIP catalyzes the creation of innovative financial tools. These tools enhance the diversity of investment strategies. Furthermore, by facilitating smoother transactions across blockchains, CCIP significantly bolsters market liquidity. This efficiency aids in the seamless exchange of tokenized assets, reducing barriers and refining price determination processes.
A collaboration between Swift, Chainlink, and significant financial entities showcased cross-chain asset transfer capabilities. Their joint effort highlights CCIP's foundational role in crafting a more inclusive and liquid financial ecosystem.
Corporate Actions: Reducing Costs and Errors
The complexity of corporate actions often leads to expensive mistakes and inefficiencies. Blockchain technology introduces a revolutionary solution by establishing a shared, immutable record. This "golden record" synchronizes all parties, curtailing potential for conflict.
The Golden Record Advantage
By serving as an unalterable ledger, blockchain drastically cuts down on corporate action inaccuracies. They have historically led to substantial financial losses. Additionally, the integration of smart contracts, powered by Chainlink's precise data, automates and simplifies operations. It's reducing the necessity for manual checks and balances.
Smart Contracts for Corporate Efficiency
Through the synergy of blockchain and Chainlink, dividend distribution becomes automated, guaranteeing precise allocations to shareholders without manual intervention. Publishing fund performance data on the blockchain ensures its reliability and immediate availability, enhancing market transparency. In the realm of proxy voting, blockchain technology offers a streamlined and transparent process, improving the accuracy of vote captures and potentially boosting participation rates among retail investors.
Blockchain and Chainlink are redefining the standards for corporate actions, showcasing their profound impact on the financial industry. They herald a future of more efficient and reliable operations.
Enjoy reading Chainlink within on-chain finance? Want to find out more about Chainlink Use Cases? Read "Chainlink in NFT and Gaming"
Conclusion
Chainlink's integration marks a significant leap in the financial domain, underpinning asset tokenization, cross-chain transfers, and streamlined corporate actions. It is instrumental in molding a digital, transparent, and inclusive financial landscape. As blockchain technology continues to be embraced, its partnership with traditional financial systems is expected to evolve, fostering a financial ecosystem that is more accessible and efficient. The trajectory of Chainlink within on-chain finance exemplifies the transformative potential of blockchain, envisioning a future where financial services are equitable, transparent, and attuned to the digital-first populace's needs.
If you are interested in utilizing Chainlink or other blockchain-based solutions for your project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com
FAQ
What role does Chainlink play in on-chain finance?
- Chainlink acts as a decentralized oracle network, bridging the gap between blockchain smart contracts and real-world data, crucial for various on-chain finance applications.
How does asset tokenization benefit from Chainlink?
- Asset tokenization with Chainlink ensures data reliability and opens up markets to wider audiences, increasing transparency and liquidity in the blockchain ecosystem.
What are the advantages of cross-chain transfers facilitated by Chainlink?
- Chainlink's Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) enhances financial inclusion and liquidity by enabling secure and efficient asset transfers across different blockchain networks.
How does Chainlink contribute to environmental sustainability in blockchain operations?
- This aspect is not directly covered in the article, but Chainlink's efficiency in data processing and smart contract execution could potentially lead to reduced energy consumption compared to traditional, more resource-intensive blockchain operations.
What measures are in place to ensure the security of Chainlink's oracle network?
- While not detailed in the article, Chainlink's security generally relies on decentralized computation to prevent single points of failure and ensure data integrity, crucial for maintaining trust in its oracle services.
 en
en  pl
pl 












