Blockchain ensures unparalleled security, transparency, and efficiency across various sectors. Within this innovative landscape, Aleph Zero and Solana have carved their niches, emerging as leading blockchain platforms. This article delves into a comparative analysis 'Aleph Zero vs Solana', aiming to illuminate their distinct features, technological advancements, and potential applications.
Understanding the Basics
Aleph Zero

- Brief History and Development: Originating from a vision to enhance privacy and scalability in blockchain, Aleph Zero quickly ascended as a notable contender. Its development team focused on creating a platform that merges traditional blockchain benefits with advanced privacy features.
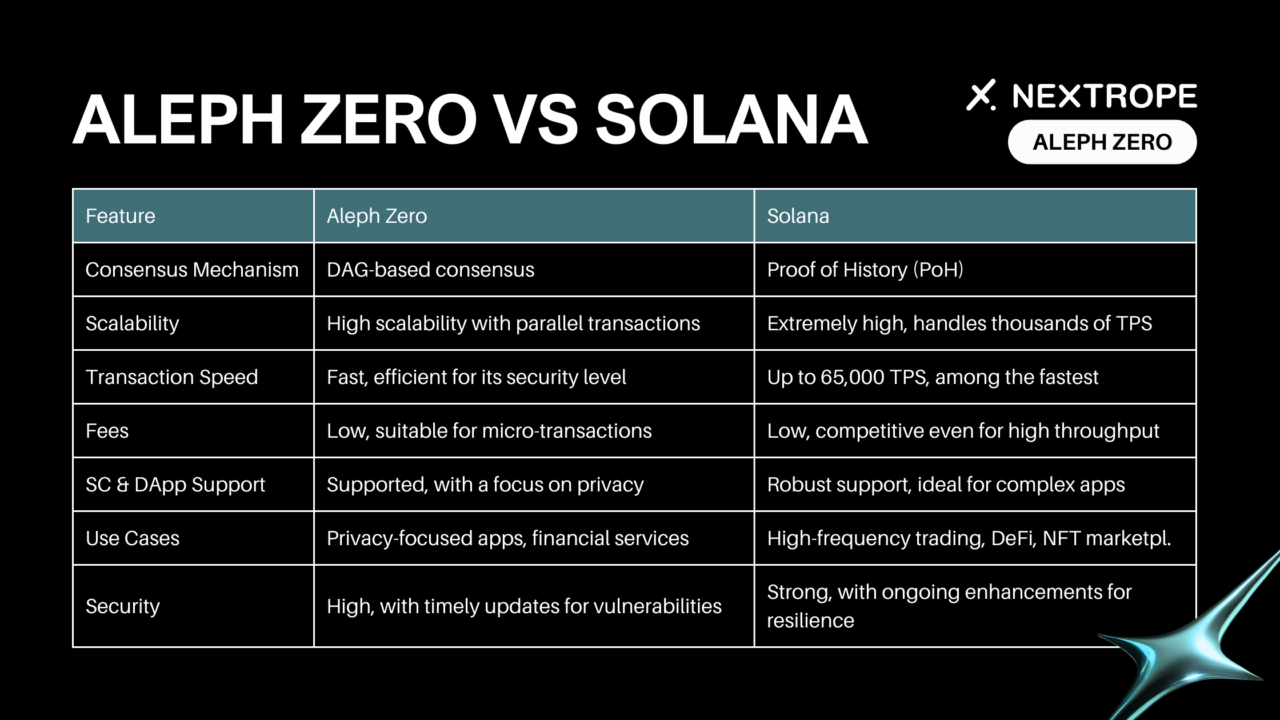
- Core Technology and Consensus Mechanism: At its core, Aleph Zero utilizes a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) combined with a unique consensus algorithm. This innovative approach not only ensures transactions are processed swiftly but also maintains high security and privacy standards.
Solana

- Brief History and Development: Solana was born from the ambition to solve the blockchain trilemma: achieving scalability, security, and decentralization without compromise. Its rapid growth is attributed to its ability to cater to high-demand applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
- Core Technology and Consensus Mechanism: Solana introduces the Proof of History (PoH) consensus mechanism, a groundbreaking innovation that allows for timestamping transactions in a sequential manner. This, combined with its underlying blockchain structure, enables Solana to process transactions at lightning speeds, setting new standards for efficiency in the blockchain domain.
The journeys of Aleph Zero and Solana, though distinct, converge on a shared goal: to redefine the capabilities of blockchain technology. Through their innovative approaches to consensus mechanisms and core technologies, both platforms offer unique solutions to the challenges facing traditional and digital markets today. Their contributions to the blockchain landscape not only highlight their individual strengths but also underscore the diverse potential of blockchain technology as a whole.
MUST READ: "What is Aleph Zero - Key Features"
Key Features Comparison - Aleph Zero vs Solana
Scalability
- Aleph Zero: Tackles scalability through its DAG-based consensus, allowing parallel transactions that increase scalability.
- Solana: Achieves high scalability with its PoH consensus, efficiently handling thousands of transactions per second (TPS).
Transaction Speed and Throughput
- Aleph Zero: Boasts fast transaction speeds due to its lightweight consensus mechanism, aiming for efficiency without sacrificing security.
- Solana: Known for its exceptional speed, Solana processes up to 65,000 TPS, setting a benchmark in blockchain throughput.
Fees
- Aleph Zero: Offers low transaction fees, making it attractive for both high-volume transactions and micro-transactions.
- Solana: Despite its high throughput, Solana maintains competitively low fees, further enhancing its appeal for developers and users alike.
Smart Contracts and DApp Development
- Aleph Zero: Supports smart contracts and DApp development, focusing on privacy and scalability within its ecosystem.
- Solana: Provides robust support for DApps and smart contracts, powered by its high-speed blockchain, ideal for complex applications.
Use Cases - Aleph Zero vs Solana
Aleph Zero
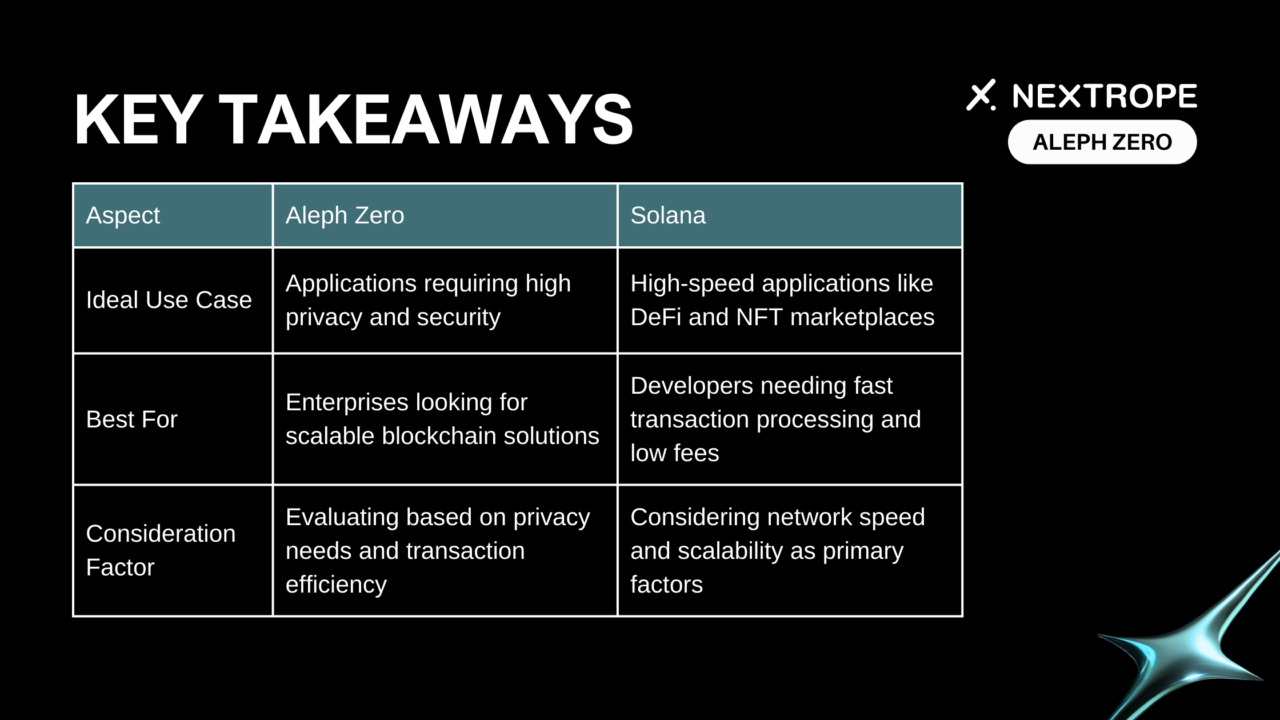
- Best Suited For: Privacy-focused applications, financial services requiring high security, and scalable enterprise solutions.
Solana
- Shines In: High-frequency trading platforms, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, and NFT marketplaces demanding fast transactions.
Performance Analysis
Network Speed and Efficiency
- Aleph Zero: Demonstrates efficiency with its innovative consensus, ensuring quick and secure transactions.
- Solana: Outpaces many with its network speed, attributed to the PoH mechanism, ensuring both rapid and consistent transaction processing.
Scalability Solutions
- Aleph Zero: Continuously explores advancements in DAG technology to enhance its scalability solutions.
- Solana: Plans to further optimize its infrastructure, ensuring it remains scalable amidst growing demand.
Security Aspects
Consensus Mechanisms
- Aleph Zero: Its unique consensus mechanism prioritizes security, aiming to prevent attacks while maintaining speed.
- Solana: Solana's PoH consensus is designed with security in mind, preventing double-spending and ensuring transaction integrity.
Known Vulnerabilities and Responses
- Aleph Zero: Responds to vulnerabilities with timely updates, emphasizing its commitment to security and privacy.
- Solana: Has faced challenges, including network congestions and DDoS attacks, but has responded with enhancements to its network resilience.
Through this comparative analysis, it becomes evident that Aleph Zero and Solana each bring distinctive strengths to the blockchain arena. Their approaches to scalability, transaction speed, fees, and smart contract capabilities cater to different needs within the blockchain ecosystem. Moreover, their targeted use cases and ongoing efforts to enhance performance and security underscore the dynamic and evolving nature of blockchain technology.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the comparative analysis between Aleph Zero vs Solana reveals two highly innovative and efficient blockchain platforms, each with its unique strengths. Aleph Zero focuses on privacy and scalability, making it ideal for applications requiring robust security measures. Solana, on the other hand, excels in transaction speed and throughput, positioning it as a top choice for high-frequency trading and DeFi applications.
If you are interested in utilizing Aleph Zero, Solana or other blockchain-based solutions for your project, please reach out to contact@nextrope.com
FAQ
What are the main differences between Aleph Zero and Solana's consensus mechanisms?
- Aleph Zero uses a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) combined with a unique consensus algorithm for high security and privacy, while Solana employs Proof of History (PoH) for high-speed transaction processing.
How do Aleph Zero and Solana compare in terms of transaction speed and scalability?
- Aleph Zero focuses on scalability with its DAG-based consensus allowing parallel transactions, while Solana is known for its exceptional speed, processing up to 65,000 transactions per second.
What are the targeted use cases for Aleph Zero and Solana?
- Aleph Zero is best suited for privacy-focused applications and scalable enterprise solutions, whereas Solana excels in high-frequency trading platforms, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, and NFT marketplaces.
How does the developer community size and support compare between Aleph Zero and Solana?
- Readers might be curious about the size of the developer community, availability of development tools, and the level of support provided to developers in both ecosystems.
What are the environmental impacts of Aleph Zero vs. Solana?
- Given increasing concerns about sustainability, potential users may question the energy consumption and environmental footprint of both blockchain platforms.
 en
en  pl
pl 












